Wounded Knee Massacre
| Wounded Knee Massacre | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the Ghost Dance War and the Sioux Wars | |||||||
 Mass grave for the Lakota dead after the massacre | |||||||
| |||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
|
|
Miniconjou Lakota Hunkpapa Lakota | ||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
|
| Spotted Elk † | ||||||
| Strength | |||||||
| 490[1] | 120[2] | ||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||
|
31 killed 33 wounded |
90 killed 4 wounded | ||||||
|
200 civilians killed 46 civilians wounded[3][4] | |||||||
Location within South Dakota | |||||||
The Wounded Knee Massacre, also known as the Battle of Wounded Knee, involved nearly three hundred Lakota people killed by soldiers of the United States Army. The massacre, part of what the U.S. military called the Pine Ridge Campaign,[5] occurred on December 29, 1890,[6] near Wounded Knee Creek (Lakota: Čhaŋkpé Ópi Wakpála) on the Lakota Pine Ridge Indian Reservation in South Dakota, following a botched attempt to disarm the Lakota camp. The previous day, a detachment of the U.S. 7th Cavalry Regiment commanded by Major Samuel M. Whitside approached Spotted Elk's band of Miniconjou Lakota and 38 Hunkpapa Lakota near Porcupine Butte and escorted them five miles (eight kilometers) westward to Wounded Knee Creek, where they made camp. The remainder of the 7th Cavalry Regiment, led by Colonel James W. Forsyth, arrived and surrounded the encampment. The regiment was supported by a battery of four Hotchkiss mountain guns.[7] The Army was catering to the anxiety of settlers who called the conflict the Messiah War and were worried the ceremonial Ghost Dance signified a potentially dangerous Sioux resurgence. Historian Jeffrey Ostler wrote in 2004, "Wounded Knee was not made up of a series of discrete unconnected events. Instead, from the disarming to the burial of the dead, it consisted of a series of acts held together by an underlying logic of racist domination."[8]
On the morning of December 29, the U.S. Cavalry troops went into the camp to disarm the Lakota. One version of events maintains that during the process of disarming the Lakota, a deaf tribesman named Black Coyote was reluctant to give up his rifle, claiming he had paid a lot for it.[9] Black Coyote's rifle went off at that point, and the soldiers began firing on the Lakota. The Lakota warriors fought back, but many had already been disarmed.[10]
More than 250 people of the Lakota were killed and 51 wounded (4 men and 47 women and children, some of whom died later). Some estimates placed the number of dead as high as 300.[3] Twenty-five soldiers also were killed and 39 were wounded (six of the wounded later died).[11] Nineteen soldiers were awarded the Medal of Honor specifically for Wounded Knee, and overall 31 for the campaign.[12][13] In 2001, the National Congress of American Indians passed two resolutions condemning the military awards and called on the federal government to rescind them.[14] The Wounded Knee National Historic Landmark, the site of the massacre, was designated a National Historic Landmark by the U.S. Department of the Interior.[6] In 1990, both houses of the U.S. Congress passed a resolution on the historical centennial formally expressing "deep regret" for the massacre.[15]
Prelude
[edit]
In the years leading up to the conflict, the U.S. government had continued to seize Lakota lands. The once-large bison herds of the Great Plains, a staple of the Plains Indians, had been hunted to near-extinction. Treaty promises[16] to protect reservation lands from encroachment by settlers and gold miners were not implemented as agreed. As a result, there was unrest on the reservations.[a] During this time, news spread among the reservations of a Paiute prophet named Wovoka, founder of the Ghost Dance religion. He had a vision that the Christian Messiah, Jesus Christ, had returned to Earth in the form of a Native American.[17]
According to Wovoka, the white invaders would disappear from Native lands, the ancestors would lead them to good hunting grounds, the buffalo herds and all the other animals would return in abundance, and the ghosts of their ancestors would return to Earth.[3] They would then live in peace. All this would be brought about by the performance of the slow and solemn Ghost Dance, performed as a shuffle in silence to a single drumbeat. Lakota ambassadors to Wovoka, Kicking Bear and Short Bull, taught the Lakota that while performing the Ghost Dance, they would wear special Ghost Dance shirts, as had been seen by Black Elk in a vision. Kicking Bear misunderstood the meaning of the shirts, and said that the shirts had the power to repel bullets.[17] Some tribes, including the Sioux, believed that a great earthquake and flood would occur which would drown all the whites.[18]
The Ghost Dance movement was a result of the slow but ever-present destruction of the Native Americans' way of life. Tribal land was being seized at alarming rates. The once numerous bison herds were nearly hunted to extinction. The entire livelihood of the plains tribes revolved around the bison, and without the resources the animal offered, their cultures rapidly lost stability and security. This forced them to rely on the United States government to provide rations and goods, or else face starvation. The way of life of these independent people was rapidly fading. The Ghost Dance brought hope: the white man would soon disappear; the buffalo herds would return; people would be reunited with loved ones who had since died; the old way of living before the white man would return. This was not just a religious movement but a response to the gradual cultural destruction.[19]
U.S. settlers were alarmed by the sight of the many Great Basin and Plains tribes performing the Ghost Dance, worried that it might be a prelude to armed attack. Among them was the U.S. Indian agent at the Standing Rock Agency where Chief Sitting Bull lived. U.S. officials decided to take some of the chiefs into custody in order to quell what they called the "Messiah craze". The military first hoped to have Buffalo Bill—a friend of Sitting Bull—aid in the plan, to reduce the chance of violence. Standing Rock agent James McLaughlin sent the Indian police to arrest Sitting Bull.[20][21][22]
On December 15, 1890, 40 Native American policemen arrived at Sitting Bull's house to arrest him. When Sitting Bull refused to comply, the police used force on him. The Lakota in the village were enraged. Catch-the-Bear, a Lakota, shouldered his rifle and shot Lt. Bullhead, who reacted by firing his revolver into the chest of Sitting Bull. Another police officer, Red Tomahawk, shot Sitting Bull in the head, and he dropped to the ground. He died between 12 and 1 p.m. After Sitting Bull's death, 200 members of his Hunkpapa band, fearful of reprisals, fled Standing Rock to join Chief Spotted Elk (later known as "Big Foot") and his Miniconjou band at the Cheyenne River Indian Reservation.[23]
Spotted Elk and his band, along with 38 Hunkpapa, left the Cheyenne River Reservation on December 23 to journey to the Pine Ridge Indian Reservation to seek shelter with Red Cloud.[24]
Former Pine Ridge Indian agent Valentine T. McGillycuddy was asked his opinion of the "hostilities" surrounding the Ghost Dance movement, by General Leonard Wright Colby, commander of the Nebraska National Guard (portion of letter dated January 15, 1891):[25]
As for the 'Ghost Dance' too much attention has been paid to it. It was only the symptom or surface indication of a deep-rooted, long-existing difficulty; as well treat the eruption of smallpox as the disease and ignore the constitutional disease.
As regards disarming the Sioux, however desirable it may appear, I consider it neither advisable, nor practicable. I fear it will result as the theoretical enforcement of prohibition in Kansas, Iowa and Dakota; you will succeed in disarming and keeping disarmed the friendly Indians because you can, and you will not succeed with the mob element because you cannot.
If I were again to be an Indian agent, and had my choice, I would take charge of 10,000 armed Sioux in preference to a like number of disarmed ones; and furthermore agree to handle that number, or the whole Sioux nation, without a white soldier. Respectfully, etc., V.T. McGillycuddy.
P.S. I neglected to state that up to date there has been neither a Sioux outbreak or war. No citizen in Nebraska or Dakota has been killed, molested or can show the scratch of a pin, and no property has been destroyed off the reservation.[26]
| General Miles's telegram | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 General Miles sent this telegram from Rapid City to General John Schofield in Washington, D.C., on December 19, 1890:[27] "The difficult Indian problem cannot be solved permanently at this end of the line. It requires the fulfillment of Congress of the treaty obligations that the Indians were entreated and coerced into signing. They signed away a valuable portion of their reservation, and it is now occupied by white people, for which they have received nothing." "They understood that ample provision would be made for their support; instead, their supplies have been reduced, and much of the time they have been living on half and two-thirds rations. Their crops, as well as the crops of the white people, for two years have been almost total failures." "The dissatisfaction is wide spread, especially among the Sioux, while the Cheyennes have been on the verge of starvation, and were forced to commit depredations to sustain life. These facts are beyond question, and the evidence is positive and sustained by thousands of witnesses." |
Fight and ensuing massacre
[edit]
After being called to the Pine Ridge Agency, Spotted Elk of the Miniconjou Lakota nation and 350 of his followers were making the slow trip to the agency on December 28, 1890, when they were met by a 7th Cavalry detachment under Major Samuel M. Whitside southwest of Porcupine Butte. John Shangreau, a scout and interpreter who was half Lakota, advised the troopers not to disarm the Lakota immediately, as it would lead to violence. The troopers escorted the Native Americans about five miles (eight kilometers) westward to Wounded Knee Creek where they told them to make camp. Later that evening, Colonel James W. Forsyth and the remainder of the 7th Cavalry arrived, bringing the number of troopers at Wounded Knee to 500.[28] In contrast, there were 350 Lakota: 120 men and 230 women and children.[9] The troopers surrounded Spotted Elk's encampment and set up four rapid-fire Hotchkiss-designed M1875 mountain guns.[29]
December 29, 1890
[edit]At daybreak on December 29, 1890, Forsyth ordered the surrender of weapons and the immediate removal of the Lakota from the "zone of military operations" to awaiting trains. A search of the camp confiscated 38 rifles, and more rifles were taken as the soldiers searched the Lakota. None of the old men were found to be armed. A medicine man named Yellow Bird allegedly harangued the young men who were becoming agitated by the search, and the tension spread to the soldiers.[30]
Specific details of what triggered the massacre are debated. According to some accounts, Yellow Bird began to perform the Ghost Dance, telling the Lakota that their "ghost shirts" were "bulletproof". As tensions mounted, Black Coyote refused to give up his rifle; he spoke no English and was deaf and had not understood the order. Another Lakota said: "Black Coyote is deaf," and when the soldier persisted, he said, "Stop. He cannot hear your orders." At that moment, two soldiers seized Black Coyote from behind, and (allegedly) in the struggle, his rifle discharged. At the same moment, Yellow Bird threw some dust into the air, and approximately five young Lakota men with concealed weapons threw aside their blankets and fired their rifles at Troop K of the 7th. After this initial exchange, the firing became indiscriminate.[31]
Eyewitness accounts state that Black Coyote's gun went off when he was seized from behind by soldiers.[32] Survivor Wasumaza, one of Big Foot's warriors who later changed his name to Dewey Beard, recalled Black Coyote was unable to hear. "If they had left him alone he was going to put his gun down where he should. They grabbed him and spinned him in the east direction. He was still unconcerned even then. He hadn't his gun pointed at anyone. His intention was to put that gun down. They came on and grabbed the gun that he was going to put down. Right after they spun him around there was the report of a gun, was quite loud. I couldn't say that anyone was shot, but following that was a crash".[33] Theodor Ragnar of the 7th Cavalry also stated that Black Coyote was deaf.[34] In contrast, a Native American named Turning Hawk called Black Coyote "a crazy man, a young man of very bad influence, and in fact a nobody."[35]

According to commanding General Nelson A. Miles, a "scuffle occurred between one deaf warrior who had [a] rifle in his hand and two soldiers. The rifle was discharged and a battle occurred, not only the warriors but the sick Chief Spotted Elk, and a large number of women and children who tried to escape by running and scattering over the prairie were hunted down and killed."[36]
Modern historians, including Dee Brown, author of Bury My Heart at Wounded Knee, have supported that Black Coyote was deaf, and that he owned a new Winchester rifle.[37]
At first all firing was at close range; half the Lakota men were killed or wounded before they had a chance to get off any shots. Some of the Lakota grabbed rifles from the piles of confiscated weapons and opened fire on the soldiers. With no cover, and with many of the Lakota unarmed, this lasted a few minutes at most. While the Lakota warriors and soldiers were shooting at close range, other soldiers used the Hotchkiss guns against the tipi camp full of women and children. It is believed that many of the soldiers were victims of friendly fire from their own Hotchkiss guns. The Lakota women and children fled the camp, seeking shelter in a nearby ravine from the crossfire.[38] The officers had lost all control of their men. Some of the soldiers fanned out and finished off the wounded. Others leaped onto their horses and pursued the Natives (men, women, and children), in some cases for miles across the prairies. In less than an hour, at least 150 Lakota had been killed and 50 wounded. Other estimates indicate nearly 300[c] of the original 350 having been killed or wounded, with a blizzard preventing immediate search following the massacre. Reports indicate that the soldiers loaded 51 survivors (4 men and 47 women and children) onto wagons and took them to the Pine Ridge Reservation.[39] Army casualties numbered 25 dead.[40] Black Coyote died at Wounded Knee.[41]
Aftermath
[edit]

Following a three-day blizzard, the military hired civilians to bury the dead Lakota. The burial party found the deceased frozen; they were gathered up and placed in a mass grave on a hill overlooking the encampment from which some of the fire from the Hotchkiss guns originated. It was reported that four infants were found alive, wrapped in their deceased mothers' shawls. In all, 84 men, 44 women, and 18 children reportedly died on the field, while at least seven Lakota were mortally wounded.[42] Miles denounced Forsyth and relieved him of command. An exhaustive Army Court of Inquiry convened by Miles criticized Forsyth for his tactical dispositions but otherwise exonerated him of responsibility. The Court of Inquiry, however, was not conducted as a formal court-martial.
The Secretary of War concurred with the decision and reinstated Forsyth to command of the 7th Cavalry. Testimony had indicated that for the most part, troops attempted to avoid non-combatant casualties. Miles continued to criticize Forsyth, whom he believed had deliberately disobeyed his commands in order to destroy the Lakota. Miles promoted the conclusion that Wounded Knee was a deliberate massacre rather than a tragedy caused by poor decisions, in an effort to destroy the career of Forsyth. This was later whitewashed, and Forsyth was promoted to brigadier, then later, major general.[43]
Many non-Lakota living near the reservations interpreted the battle as the defeat of a murderous cult; others confused Ghost Dancers with Native Americans in general. In an editorial response to the event, the young newspaper editor L. Frank Baum, later the author of The Wonderful Wizard of Oz, wrote in The Aberdeen Saturday Pioneer on January 3, 1891:
The Pioneer has before declared that our only safety depends upon the total extermination of the Indians. Having wronged them for centuries, we had better, in order to protect our civilization, follow it up by one more wrong and wipe these untamed and untamable creatures from the face of the earth. In this lies future safety for our settlers and the soldiers who are under incompetent commands. Otherwise, we may expect future years to be as full of trouble with the redskins as those have been in the past.[44]
Soon after the event, Dewey Beard, his brother Joseph Horn Cloud, and others formed the Wounded Knee Survivors Association, which came to include descendants. They sought compensation from the U.S. government for the many fatalities and injured. Today the association is independent and works to preserve and protect the historic site from exploitation, and to administer any memorial erected there. Papers of the association (1890–1973) and related materials are held by the University of South Dakota and are available for research.[45] It was not until the 1990s that a memorial to the Lakota was included in the National Historic Landmark. In 1968 James Czywczynski purchased 40 acres of property adjacent to Wounded Knee, operating a trading post and museum.[46]
More than 80 years after the massacre, beginning on February 27, 1973, Wounded Knee was the site of the Wounded Knee incident, a 71-day standoff between militants of the American Indian Movement—who had chosen the site for its symbolic value—and federal law enforcement officials.[47] Among the buildings destroyed were the Czywczynski post and Museum; the Czywczynskis moved away asking a purchase price of $3.9 million [land appraised at $14,000]. On September 7, 2022, the Oglala Sioux tribal council and the Cheyenne River Sioux Tribe voted to buy for $500,000 the 40-acre site from the Czywczynskis. (The Oglala Sioux tribal already owned one acre of Land from Wounded Knee which was donated by the Red Cloud Indian school on the site of the Sacred Heart church had stood.)[46]
Stranded 9th Cavalry
[edit]The battalion of 9th Cavalry was scouting near the White River (Missouri River tributary) about 15 miles (24 kilometers) north of Indian agency at Pine Ridge when the Wounded Knee Massacre occurred and rode south all night to reach the reservation. In the early morning of December 30, 1890, F, I, and K Troops reached the Pine Ridge agency, however, their supply wagon guarded by D Troop located behind them was attacked by 50 Lakota warriors near Cheyenne Creek (about 2 mi or 3 km from the Indian agency). One soldier was immediately killed. The wagon train protected itself by circling the wagons. Corporal William Wilson volunteered to take a message to the agency at Pine Ridge to get help after the Indian scouts refused to go. Wilson took off through the wagon circle with Lakota in pursuit and his troops covering him. Wilson reached the agency and spread the alarm. The 9th Cavalry within the agency came to rescue the stranded troopers and the Lakota dispersed. For his actions, Corporal Wilson received the Medal of Honor.[48]
Drexel Mission Fight
[edit]
Historically, Wounded Knee is generally considered to be the end of the collective multi-century series of conflicts between colonial and U.S. forces and American Indians, known collectively as the Indian Wars. It was not however the last armed conflict between Native Americans and the United States.[49]
The Drexel Mission Fight was an armed confrontation between Lakota warriors and the United States Army that took place on the Pine Ridge Indian Reservation on December 30, 1890, the day following Wounded Knee. The fight occurred on White Clay Creek approximately 15 miles (24 kilometers) north of Pine Ridge, where Lakota fleeing from the continued hostile situation surrounding the massacre at Wounded Knee had set up camp.[31][page needed]
Company K of the 7th Cavalry—the unit involved at Wounded Knee—was sent to force the Lakotas to return to the areas they were assigned on their respective reservations. Some of the "hostiles" were Brulé Lakota from the Rosebud Indian Reservation. Company K was pinned down in a valley by the combined Lakota forces and had to be rescued by the 9th Cavalry, an African American regiment nicknamed the "Buffalo Soldiers".[50]
Among the Lakota warriors was a young Brulé from Rosebud named Plenty Horses, who had recently returned from five years at the Carlisle Indian School in Pennsylvania. A week after this fight, Plenty Horses shot and killed army lieutenant Edward W. Casey,[51] commandant of the Cheyenne Scouts (Troop L, 8th Cavalry). The testimony introduced at the trial of Plenty Horses and his subsequent acquittal also helped abrogate the legal culpability of the U.S. Army for the deaths at Wounded Knee.[52]
Winter guards
[edit]The 9th Cavalry were stationed on the Pine Ridge reservation through the rest of the winter of 1890–1891 until March 1891. By then, the 9th Cavalry was the only regiment on the reservation after being the first to arrive in November 1890.[48]
Medals of Honor
[edit]For this 1890 campaign, the US Army awarded 31 Medals of Honor, 19 specifically for service at Wounded Knee.[12][13][53]
In the Nebraska State Historical Society's summer 1994 quarterly journal, Jerry Green construes that pre-1916 Medals of Honor were awarded more liberally; however, "the number of medals does seem disproportionate when compared to those awarded for other battles." Quantifying, he compares the three awarded for the Battle of Bear Paw Mountain's five-day siege, to the twenty awarded for this short and one-sided action.[54] Historian Will G. Robinson notes that, in contrast, only three Medals of Honor were awarded among the 64,000 South Dakotans who fought for four years of World War II.[55] However, historian Dwight Mears points out that awards prior to 1918 were "Medal[s] of Honor in name only," making such comparisons with modern medals inappropriate, since "the medal that existed in 1890 is a materially different award."[56]
Native American activists have urged the medals be withdrawn, calling them "medals of dishonor". According to Lakota tribesman William Thunder Hawk, "The Medal of Honor is meant to reward soldiers who act heroically. But at Wounded Knee, they didn't show heroism; they showed cruelty." In 2001, the National Congress of American Indians passed two resolutions condemning the Medals of Honor awards and called on the U.S. government to rescind them.[14]
A number of the citations on the medals awarded to the troopers at Wounded Knee state that they went in pursuit of Lakota who were trying to escape or hide.[57] Another citation was for "conspicuous bravery in rounding up and bringing to the skirmish line a stampeded pack mule."[54] Another medal was awarded in part for extending an enlistment.[58]
In February 2021, the South Dakota Senate unanimously called upon the United States Congress to investigate the 20 medals of honor awarded to members of the 7th Cavalry for their participation in the massacre. Lawmakers argued that the medals given to the soldiers of the 7th Cavalry Regiment tarnished Medals of Honor given to soldiers for genuine acts of courage. Previous efforts to rescind the medals have failed.[59] In March 2021, Senators Elizabeth Warren (D-MA) and Jeff Merkley (D-OR) and Congressman Kaiali'i Kahele (D-HI) answered the South Dakota Senate's call and reintroduced a bill to revoke the Medals of Honor awarded to the soldiers who perpetrated the Wounded Knee massacre.[60] The provision was incorporated into the FY2022 National Defense Authorization Act, but was removed in conference with the explanation that "these Medals of Honor were awarded at the prerogative of the President of the United States, not the Congress."[61] This effectively expressed that since adjudication authority was granted to the executive, that it was not the role of Congress to revoke medals. As a result, the bill failed due to a separation of powers conflict.[62] An identical version of Remove the Stain was added to the National Defense Authorization Act for Fiscal Year 2023 (2022), however, it was again removed from the final version of the defense bill by the Senate Armed Services Committee.[63] The Remove the Stain Act also failed to identify an effective process of revocation, stipulating in error that the recipients would be removed from the Medal of Honor Roll. However, none of the Wounded Knee medal recipients were on the Medal of Honor Roll, which was a pension list.[62]
In July 2024, the Secretary of Defense announced a joint DoD/DoI review to consider revoking the Wounded Knee Medals of Honor. [64] Notably, the DoD review cited the joint explanatory statement for the FY2022 National Defense Authorization Act (which removed the Remove the Stain Act from the bill) as the impetus for the medal review.[64]
| Medal of Honor citations, Wounded Knee[65] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Remembrance
[edit]Commemoration of Native American deaths
[edit]
In 1891 The Ghost Shirt, thought to have been worn by one who died in the massacre, was brought to Glasgow, Scotland, by George C Crager, a Lakota Sioux interpreter with Buffalo Bill's Wild West Show. He sold it to the Kelvingrove Museum, which displayed the shirt until it was returned to Wounded Knee Survivors Association in 1998.[68]
St. John's Episcopal Mission Church was built on the hill behind the mass grave in which the victims had been buried, some survivors having been nursed in the then-new Holy Cross Mission Church.[69] In 1903, descendants of those who died in the battle erected a monument at the gravesite. The memorial lists many of those who died at Wounded Knee along with an inscription that reads:
This monument is erected by surviving relatives and other Ogalala and Cheyenne River Sioux Indians in memory of the Chief Big Foot massacre December 29, 1890. Col. Forsyth in command of US troops. Big Foot was a great chief of the Sioux Indians. He often said, 'I will stand in peace till my last day comes.' He did many good and brave deeds for the white man and the red man. Many innocent women and children who knew no wrong died here.[70]
Wounded Knee was declared a U.S. National Historic Landmark in 1965 and was listed on the U.S. National Register of Historic Places in 1966.
Beginning in 1986, the group named "Big Foot Memorial Riders" was formed where they will go to continue to honor the dead. The ceremony has attracted more participants each year and riders and their horses live with the cold weather, as well as the lack of food and water, as they retrace the path that their family members took to Wounded Knee. They carry with them a white flag to symbolize their hope for world peace, and to honor and remember the victims so that they will not be forgotten.[42]
Seventh Cavalry Regiment
[edit]When the 7th Cavalry Regiment returned to duty at Fort Riley from Pine Ridge, South Dakota, the soldiers of the regiment raised money for a monument for members of the regiment killed at Wounded Knee. About $1,950[clarification needed] was collected, and on July 25, 1893, the monument was dedicated with 5,500 people in attendance. The stone edifice stands near Waters Hall.[71]
Wounded Knee as worst mass shooting in the history of the United States
[edit]Many popular media sources write about the event as "The worst mass shooting" in United States history, though the term "mass shooting" lacks any clear definition.[72] Often the distinction as "worst mass shooting" is compared to other mass shootings in the United States after a mass casualty event involving a single shooter and numerous dead, whereas the Wounded Knee Massacre involved numerous shooters from the United States government of unarmed Lakota men, women, and children.[73][74] Often after a mass shooting in the United States after it becomes known how many people have died due to the firearm related fatality, a comparison to other mass shootings might be reported on in the media,[75] at this point, some critics point out that the Wounded Knee massacre is sometimes forgotten in place of more recent mass shootings, either as a result of:
- Wounded Knee having occurred more in the distant past,
- The United States government having perpetrated the Wounded Knee shooting instead of a lone wolf or private civilian shooters, or;
- Media attention tending to "...gloss over Native American massacres..."[76]
Largely the phenomena using the "mass shooting" language, and subsequent comparison to other shootings, is most widely reported on in the United States.[75]
Order of battle
[edit]



7th U.S. Cavalry[1]
Col James W. Forsyth
- Adjutant: 1st Lt. Lloyd S. McCormick
- Quartermaster: 1st Lt. Ezra B. Fuller
- Assistant Surgeon & Medical Director: Cpt. John Van Rennselaer Hoff
- Assistant Surgeon: 1st Lt. James Denver Glennan
First Squadron
Maj Samuel Whitside
- Adjutant: 1st Lt. William Jones Nicholson
- Troop A: Cpt. Myles Moylan, 1st Lt. Ernest A. Garlington
- Troop B: Cpt. Charles A. Varnum, 1st Lt. John C. Gresham
- Troop I: Cpt. Henry J. Nowlan, 2nd Lt. John C. Waterman
- Troop K: Cpt. George D. Wallace (k), 1st Lt. James D. Mann
Second Squadron
Cpt. Charles S. Isley
- Adjutant: 1st Lt. W.W. Robinson II
- Troop C: Cpt. Henry Jackson, 2nd Lt. T.Q. Donaldson
- Troop D: Cpt. Edward S. Godfrey, 2nd Lt. S.R.J. Tompkins
- Troop E: Cpt. Charles S. Isley, 1st Lt. Horatio G. Sickel, 2nd Lt. Sedgwick Rice
- Troop G: Cpt. Winfield S. Edgerly, 1st Lt. Edwin P. Brewer
Battery E, 1st U.S. Artillery
Captain Allyn Capron
- 2nd Lt. Harry L. Hawthorne (2nd U.S. Artillery)
- 4 Hotchkiss Breech-Loading Mountain Rifles
Troop A, Indian Scouts
- 1st Lt. George W. Taylor (9th U.S. Cavalry)
- 2nd Lt. Guy H. Preston (9th U.S. Cavalry)
Lakota[1]
120 men, 230 women and children[10]
Gallery
[edit]-
Miniconjou Lakota dance at Cheyenne River, South Dakota, August 9, 1890
-
Holy Cross Episcopal Mission, used as hospital for wounded Lakota
-
Photographer taking pictures of campsite
-
Frozen corpse on field
-
Photograph sold as being that of the Medicine Man "Yellow Bird"; the presence of the rifle however suggests that it is actually the body of "Black Coyote"
-
The scene three weeks afterwards, with several bodies partially wrapped in blankets in the foreground.
-
Buffalo Bill, Capt. Baldwin, Gen. Nelson A. Miles, Capt. Moss, and others, on horseback, on battlefield of Wounded Knee.
-
Gen. L. W. Colby holding Zintkála Nuni (Little Lost Bird), found alive on the snow-covered Wounded Knee field four days after the massacre, still tied to her dead mother's back
-
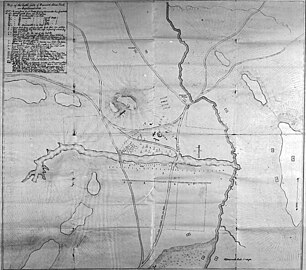
Map of Wounded Knee battlefield scene produced by James W. Forsyth (1834– 1906)
-
1858 War Department map of the Great Plains; Fort Laramie is marked with a red flag, Wounded Knee Creek is visible between the S and the K in Nebraska
-
Excerpt of Burlington Route map produced 1892, showing site of Wounded Knee and Deadwood Central Railroad into the Black Hills
-
"Map of the country embraced in the campaign against the Sioux Indians Messiah War" (1905)
-
North Dakota and South Dakota map 1 (of 3) from Indian Land Cessions in the United States (1898)
-
Map of the Great Sioux Reservation
-
Reenactment of U.S. troops surrounding the Lakota at Wounded Knee (1913).
-
Wounded Knee, 1940
-
Wounded Knee grave, 2003
-
US Attorney General Eric Holder laying a wreath at the site of the Wounded Knee Memorial
In popular culture
[edit]Massacre or battle
[edit]
The incident was initially referred to as the "Battle of Wounded Knee".[77] Some Native American groups have objected to this description and refer to it as the "Wounded Knee Massacre". The location of the conflict is officially known as the "Wounded Knee Battlefield". The U.S. Army currently refers to it as "Wounded Knee".[57]
Bury my heart at Wounded Knee
[edit]In his 1931 poem "American Names", Stephen Vincent Benét coined the phrase "Bury my heart at Wounded Knee". The poem is about his love of American place names, not making reference to the "battle".[78] When the line was used as the title of historian Dee Brown's 1970 best-selling book, awareness was raised and Benet's phrase became popularly associated with the incident.
Since the publication of the book, the phrase "Bury my heart at Wounded Knee" has been used many times in reference to the battle, especially in music.
In 1972, Robbie Basho released the song "Wounded Knee Soliloquy" on the album The Voice of the Eagle.
In 1973, Stuttgart, Germany's Gila released a krautrock/psychedelic folk album by the same name.
In 1992, Beverly (Buffy) Sainte-Marie released her song titled "Bury My Heart at Wounded Knee" on Coincidence and Likely Stories.
In other music
[edit]Artists who have written or recorded songs referring to the battle at Wounded Knee include: Walela "Wounded Knee" from the 1997 self-titled album. Nightwish ("Creek Mary's Blood" from their 2004 album "Once" featuring John Two-Hawks); Manowar ("Spirit Horse Of The Cherokee" from the 1992 album The Triumph Of Steel ); Grant Lee Buffalo ("Were You There?" from the album Storm Hymnal 2001); Johnny Cash (1972's "Big Foot", which is strongly sympathetic); Gordon Lightfoot ("Protocol" from his 1976 album Summertime Dream); Indigo Girls (a 1995 cover of Sainte-Marie's song); Charlie Parr ("1890" on his 2010 album When the Devil Goes Blind); Nik Kershaw ("Wounded Knee" on his 1989 album The Works); 1982 Single by Southern Death Cult ("Moya"); The Waterboys ("Bury My Heart"); Uriah Heep; Primus; Nahko and Medicine for the People; Patti Smith;[79] Robbie Robertson;[80] Five Iron Frenzy wrote the 2001 song "The Day We Killed" with mentions of Black Kettle, and quotes Black Elk's account from Black Elk Speaks on the album Five Iron Frenzy 2: Electric Boogaloo; Toad the Wet Sprocket; Marty Stuart; Bright Eyes; and "Pocahontas" by Neil Young. On Sam Roberts' 2006 Chemical City album, the song "The Bootleg Saint" contains line critical of Knee Massacre.[81] There is also a Welsh song titled "Gwaed Ar Yr Eira Gwyn" by Tecwyn Ifan on this incident. The song "American Ghost Dance" by the Red Hot Chili Peppers makes extensive reference to the massacre as well.
In 1973, the American rock band Redbone, formed by Native Americans Patrick and Lolly Vasquez, released the song "We Were All Wounded at Wounded Knee". The song ends with the subtly altered sentence "We were all wounded by Wounded Knee."[82] The song reached the number-one chart position across Europe. In the U.S., the song was initially withheld from release and then banned by several radio stations. Richard Stepp's 2008 Native American Music Awards Native Heart nominated album The Sacred Journey,[83] has "Wounded Knee" as its final track.
In film
[edit]The massacre has been referred to in films, including Thunderheart (1992), Legends of the Fall (1994), Hidalgo (2004), and Hostiles (2017). The 2005 TNT mini-series Into the West included scenes of the massacre. In 2007, HBO Films released a film adaptation of the Dee Brown bestseller Bury My Heart at Wounded Knee. The 2016 film Neither Wolf Nor Dog has its climax at the massacre site and was filmed on location there.[84]
Other
[edit]In the 1992 video game Teenage Mutant Ninja Turtles: Turtles in Time, one level is called "Bury My Shell at Wounded Knee." It takes place in 1885 AD on a train in the Old American West.
In the 1996 DC comic book Saint of Killers, written by Garth Ennis, the main character becomes a surrogate Angel of Death, reaping souls whenever men kill other men violently. The story is set in the 1880s, and near the end of chapter 4, it is said that "four years later" he was called upon at Wounded Knee.
In the 2013 video game BioShock Infinite, several main characters are veterans of Wounded Knee.[85] The protagonist, Booker DeWitt, is haunted by his deeds during the battle and at one point confronts one of his (fictional) superiors from the event.[86]
The Wounded Knee Massacre, and the events leading to it, constitute the final chapter of Złoto Gór Czarnych (Gold of the Black Hills), a trilogy of novels told from the perspective of the Santee Dakota tribe by Polish author Alfred Szklarski and his wife Krystyna Szklarska.
See also
[edit]- Wounded Knee Incident (1973)
- Indian massacres in the United States
- Genocide of indigenous peoples
- History of South Dakota
- Native American genocide in the United States
- Plains Indians Wars
- Manifest Destiny
- Wounded Knee of Alaska
- Thomas Quinton Donaldson Jr.
Notes
[edit]- ^ To this day, the Sioux have refused to accept compensation for the Black Hills land seized from them. A 1980 Supreme Court decision (United States v. Sioux Nation of Indians) ruled the taking was illegal and awarded compensation, increased by interest to $757 million, but not the return of the land which the Sioux sought. The Lakota have refused to take the money, demanding instead the return of the land.
- ^ The photographer John C. H. Grabill's caption on the original photograph in the Library of Congress reads: "No.3627. Famous Battery "E" of the 1st Artillery. These brave men and the Hotchkiss guns that Big Foot's Indians thought were toys, Together with the fighting 7th what's left of Gen. Custer's boys, Sent 200 Indians to that Heaven which the ghost dancer enjoys. This checked the Indian noise, and Gen. Miles with staff Returned to Illinois. Photo and copyright by Grabilll ,'91. Deadwood, S.D."
- ^ Derived from Nelson Miles' report of some 300 snow-covered forms during his inspection of the field three days later, Miles in a letter states: "The official reports make the number killed 90 warriors and approximately 200 women and children."
References
[edit]- ^ a b c Utley (2004), p. 201.
- ^ Brown (2009), p. 178, Brown states that at the army camp, "the Indians were carefully counted." Utley (2004), p. 204, gives 120 men, 230 women and children; there is no indication how many were warriors, old men, or incapacitated sick like Foot.
- ^ a b c "Plains Humanities: Wounded Knee Massacre". Archived from the original on December 10, 2014. Retrieved December 9, 2014.
resulted in the deaths of more than 250, and possibly as many as 300, Indians.
- ^ Nelson A. Miles to the Commissioner of Indian Affairs, March 13, 1917, "The official reports make the number killed 90 warriors and approximately 200 women and children."
- ^ Greene, Jerome A. (January 31, 2007). Indian War Veterans: Memories of Army Life and Campaigns in the West, 1864–1898. Savas Beatie. p. 193. ISBN 978-1-61121-022-4.
- ^ a b "National Historic Landmarks Program: Wounded Knee". National Park Service. Archived from the original on January 10, 2003. Retrieved January 10, 2008.
- ^ Liggett, Lorie (1998). "Wounded Knee Massacre – An Introduction". Bowling Green State University. Archived from the original on October 30, 2000. Retrieved March 2, 2007.
- ^ PRUCHA, FRANCIS PAUL (2005). Ostler, Jeffrey (ed.). "Wounded Knee through the Lens of Colonialism". Diplomatic History. 29 (4): 725–728. doi:10.1111/j.1467-7709.2005.00512.x. ISSN 0145-2096. JSTOR 24915067.
- ^ a b Parsons, Randy. "The Wounded Knee Massacre – December 1890". Lastoftheindependents.com. Archived from the original on January 6, 2010. Retrieved August 17, 2011.
- ^ a b "PBS – The West – Like Grass Before the Sickle". www.pbs.org.
- ^ Jack Utter (1991). Wounded Knee & the Ghost Dance Tragedy (1st ed.). National Woodlands Publishing Company. p. 25. ISBN 0-9628075-1-6.
- ^ a b Greene, Jerome A. (2014). American Carnage: Wounded Knee, 1890. Norman, OK: University of Oklahoma Press. pp. 417–418. ISBN 978-0-8061-4448-1.
- ^ a b "An alternative proposal for the Wounded Knee medal problem". January 3, 2024.
- ^ a b "Lakota~WOUNDED KNEE: A Campaign to Rescind Medals: story, pictures and information". Footnote.com. Archived from the original on December 31, 2013. Retrieved August 17, 2011.
- ^ AP (October 29, 1990). "Congress Adjourns – Century Afterward, Apology For Wounded Knee Massacre". The New York Times. Pine Ridge Indian Reservation (Sd); United States. Retrieved July 26, 2016.
- ^ Hall, Kermit L (ed.), The Oxford Guide to the Supreme Court of the United States, Oxford Press, 1992; section: "Native Americans," p. 580 ISBN 0-19-505835-6
- ^ a b "Wovoka". PBS: New Perspectives on the West. Archived from the original on April 4, 2011. Retrieved August 6, 2010.
- ^ James Mooney (1880). "The Ghost-Dance Religion and the Sioux Outbreak of 1890". Annual Report of the Bureau of Ethnology to the Secretary of the Smithsonian Institution 14th. 2: 788.
- ^ Lesser, Alexander (1933). "Cultural Significance of The Ghost Dance". American Anthropologist. 35 (1): 108–115. doi:10.1525/aa.1933.35.1.02a00090. JSTOR 662367.
- ^ "10 Things You May Not Know About Sitting Bull". HISTORY. July 10, 2023. Retrieved October 14, 2023.
- ^ "Sitting Bull killed by Indian police". HISTORY. Retrieved October 14, 2023.
- ^ "Digital History". www.digitalhistory.uh.edu. Retrieved October 14, 2023.
- ^ "Bigfoot Pass Overlook". U.S. National Park Service. Retrieved October 14, 2023.
- ^ Viola, Herman J. Trail to Wounded Knee: The Last Stand of the Plains Indians 1860–1890. Washington, DC: National Geographic Society, 2003.
- ^ Annual report, Part 2 By Smithsonian Institution. Bureau of American Ethnology, John Wesley Powell, Matthew Williams, pp. 831–833 (1896)
- ^ The ghost-dance religion and the Sioux outbreak of 1890, by James Mooney, p. 833
- ^ United States Congress (1937). Hearings Before the Committee on Indian Affairs. U.S. Government Printing Office. p. 28. Archived from the original on February 13, 2021. Retrieved December 28, 2017.
- ^ Russell, Major Samuel L., "Selfless Service: The Cavalry Career of Brigadier General Samuel M. Whitside from 1858 to 1902." MMAS Thesis, Fort Leavenworth: U.S. Command and General Staff College, 2002.
- ^ Axelrod, Alan. (1993) Chronicles of the Indian Wars: From Colonial Times to Wounded Knee. (p. 254).
- ^ Utley (2004), p. 211.
- ^ a b Utley, Robert M. (1963). The Last Days of the Sioux Nation. New Haven, CT: Yale University Press. ISBN 0300103166. Archived from the original on February 13, 2021. Retrieved August 4, 2007.[page needed]
- ^ Utley, Robert Marshall (2004). The Last Days of the Sioux Nation (2nd ed.). Yale University Press. p. 212. ISBN 978-0-300-10316-8. Archived from the original on February 13, 2021. Retrieved February 13, 2021.
- ^ "On the 120th Anniversary of Wounded Knee". National Institute of the American Indian. Smithsonian Institution. Archived from the original on February 13, 2021. Retrieved September 28, 2020.
- ^ Grua, David W. (2016). Surviving Wounded Knee : the Lakotas and the politics of memory. Oxford: Oxford University Press. pp. 124–125. ISBN 978-0-19-024903-8. OCLC 921821850.
- ^ Charlton, Linda (December 30, 1975). "Army Denies a Wounded Knee Massacre". The New York Times. p. 16. Archived from the original on July 23, 2018. Retrieved August 6, 2009.
- ^ Phillips, Charles. December 29, 1890. American History. December 2005 40(5) pp. 16–68.
- ^ Brown, Dee (2009). Bury My Heart at Wounded Knee: An Indian History of the American West (Illustrated ed.). New York and Toronto: Sterling Publishing. pp. 521–522. ISBN 978-1-4027-6066-2.
- ^ Bateman, Robert (June 2008). "Wounded Knee". Military History. 24 (4): 62–67.
- ^ Brown (2009), pp. 179–180.
- ^ "U.S. Army Massacres Sioux Indians at Wounded Knee". HISTORY. Retrieved October 14, 2023.
- ^ "An Old Dilemma: What about the Indians? Militants vs. Tribal Leaders". The Los Angeles Times. March 11, 1973. p. 86. Archived from the original on February 13, 2021. Retrieved September 29, 2020.
- ^ a b Josephy, Jr., Alvin M., Trudy Thomas, and Jeanne Eder. Wounded Knee: Lest We Forget. Billings, Montana: Buffalo Bill Historical Center, 1990.
- ^ Ostler, Jeffrey. (2004) The Plains Sioux and U.S. Colonialism from Lewis and Clark to Wounded Knee. (p. 354).
- ^ Giago, Tim (Nanwica Kciji). "The Man Who Called for the Extermination of the Lakota" Archived February 13, 2021, at the Wayback Machine, Notes from Indian Country © 2014 Native Sun News, at HuffPost. Retrieved July 15, 2018.
- ^ "Wounded Knee Survivors Association, Papers (1890–1973)" Archived March 24, 2012, at the Wayback Machine, Archives and Special Collections, University of South Dakota, accessed June 7, 2011
- ^ a b Mary Annette Palmer (September 9, 2022). "Wounded Knee land comes home at last". Indian Country Today.
- ^ James Parsons (March 25, 1973). "AIM Indians with 'story to tell' made Wounded Knee the medium". Minneapolis Tribune.
Via Ben Welter (October 15, 2007). "Sunday, March 25, 1973: Inside Wounded Knee". startribune.com/blogs. Star Tribune. Archived from the original on June 22, 2008. Retrieved December 28, 2013. - ^ a b Schubert, Frank N. (1997). Black Valor: Buffalo Soldiers and the Medal of Honor, 1870–1898. Scholarly Resources Inc. pp. 121–132. ISBN 978-0842025867.
- ^ Hedin, Benjamin; Estes, Nick (May 6, 2023). "The Siege of Wounded Knee Was Not an End but a Beginning". The New Yorker. ISSN 0028-792X. Retrieved October 14, 2023.
- ^ Jeffrey Ostler: The Plains Sioux and U.S. colonialism from Lewis and Clark to Wounded Knee, pp. 357–358, Cambridge University Press (2004) ISBN 0-521-60590-3
- ^ Congressional edition By United States. Congress, p. 132. April 26, 2011. Archived from the original on February 13, 2021. Retrieved August 17, 2011.
- ^ Roger L. Di Silvestro: In the Shadow of Wounded Knee: The Untold Final Story of the Indian Wars, p. 198, Walker & Company (2007) ISBN 0-8027-1514-1
- ^ Dwight S. Mears, "Removing the Stain Without Undermining Military Awards: Revoking Medals Earned at Wounded Knee Creek in 1890," American Indian Law Review 48 (No. 1): 179-216. https://digitalcommons.law.ou.edu/ailr/vol48/iss1/7/
- ^ a b Green, Jerry (1994). "The Medals of Wounded Knee" (PDF). Nebraska History. Vol. 75. Nebraska State Historical Society. pp. 200–208. Archived from the original on June 29, 2017. Retrieved July 1, 2019.
- ^ "Doctor Sally Wagner Testifies At Wounded Knee Hearings Part Two". First Nations/First Peoples Issues. Archived from the original on July 8, 2018.
- ^ Dwight S. Mears, "Removing the Stain Without Undermining Military Awards: Revoking Medals Earned at Wounded Knee Creek in 1890," American Indian Law Review 48 (No. 1): 194. https://digitalcommons.law.ou.edu/ailr/vol48/iss1/7/
- ^ a b "Medal of Honor Recipients – Indian Wars Period". Medal of Honor. U.S. Army Center of Military History. Archived from the original on May 18, 2017. Retrieved August 17, 2011.
- ^ Dwight S. Mears, "Removing the Stain Without Undermining Military Awards: Revoking Medals Earned at Wounded Knee Creek in 1890," American Indian Law Review 48 (No. 1): 211. https://digitalcommons.law.ou.edu/ailr/vol48/iss1/7/
- ^ "S. Dakota Senate unanimously seeks inquiry into Wounded Knee Medals of Honor". Daily Kos. February 23, 2021. Retrieved February 27, 2021.
That wasn't a battle, that was a slaughter.
- ^ "Warren, Merkley, and Kahele Reintroduce the Remove the Stain Act" (Press release). Elizabeth Warren. March 26, 2021.
- ^ Joint Explanatory Statement to Accompany the National Defense Authorization Act for Fiscal Year 2022 (2021), pp. 131–132.
- ^ a b Mears, Dwight (January 1, 2024). "Removing the Stain Without Undermining Military Awards: Revoking Medals Earned at Wounded Knee Creek in 1890". American Indian Law Review. 48 (1): 179. ISSN 1930-7918.
- ^ Dwight S. Mears, "Removing the Stain Without Undermining Military Awards: Revoking Medals Earned at Wounded Knee Creek in 1890," American Indian Law Review 48 (No. 1): 199. https://digitalcommons.law.ou.edu/ailr/vol48/iss1/7/
- ^ a b "Austin Orders Review of Wounded Knee Medals".
- ^ Hill, Richard (October 7, 1999). "Wounded Knee, A Wound That Won't Heal". First Nations issues of consequence. Archived from the original on February 13, 2021. Retrieved April 23, 2015.
- ^ War Dept. General Orders No. 100, Dec. 17, 1891.
- ^ Dwight S. Mears, "Removing the Stain Without Undermining Military Awards: Revoking Medals Earned at Wounded Knee Creek in 1890," American Indian Law Review 48 (No. 1): 195. https://digitalcommons.law.ou.edu/ailr/vol48/iss1/7/
- ^ "Statue to Wild West showman Cody". BBC News. November 17, 2006. Archived from the original on February 13, 2021. Retrieved April 14, 2020.
- ^ "History of Holy Cross Church Pine Ridge, SD". freepages.rootsweb.com.
- ^ Utley (2004), p. 5.
- ^ Mackale, William and Robert Smith(2003) "Images of America: Fort Riley". Retrieved January 11, 2014.
- ^ Laura J. Nelson (June 15, 2016). "The worst mass shooting? A look back at massacres in U.S. history". Los Angeles Times. Retrieved October 14, 2023.
- ^ "The Worst Mass Shooting in U.S. History Was Not in Orlando". Big Think. June 14, 2016. Retrieved October 14, 2023.
- ^ Mike Anderson (June 19, 2016). "Wounded Knee, and the bloody history of mass shootings in the US". Rapid City Journal. Retrieved October 14, 2023.
- ^ a b Letters (October 5, 2017). "Deadliest mass shooting in modern US history – Wounded Knee, not Las Vegas". The Guardian. ISSN 0261-3077. Retrieved December 7, 2023.
- ^ Kale Williams (June 13, 2016). "Orlando headlines gloss over Native American massacres". Oregonian/OregonLive. Retrieved October 14, 2023.
- ^ "American soldiers gathering up dead Sioux Indians after the Wounded Knee Massacre in South Dakota, 1892". USC Digital Library (Photograph Annotation). Archived from the original on May 30, 2014. Retrieved November 14, 2023.
- ^ Izzo, David Garrett; Konkle, Lincoln (2002). Stephen Vincent Benet: Essays on His Life and Work. McFarland. p. 120. ISBN 978-0786413645. Archived from the original on February 13, 2021. Retrieved December 29, 2017.
- ^ Patti Smith Group, "Ghost Dance". On Easter, Arista AB 4171, released 1978.
- ^ Robbie Robertson, "Ghost Dance", on Music for the Native Americans, Cema/Capitol 28295, 1994.
- ^ Sam Roberts. "Sam Roberts – The Bootleg Saint Lyrics MetroLyrics". MetroLyrics. Archived from the original on February 13, 2021. Retrieved October 8, 2013.
- ^ "Discography: We are[sic] all wounded at Wounded Knee". Redbone. Archived from the original on December 31, 2013. Retrieved March 31, 2010. Unofficial discography site, with lyrics.
- ^ "NAMA 10". NativeAmericanMusicAwards.com. Native American Music Awards. 2008. Archived from the original on February 13, 2021. Retrieved December 30, 2013.
- ^ "Hocak Worak". www.hocakworak.com. Archived from the original on February 13, 2021. Retrieved October 2, 2019.
- ^ Goldfarb, Andrew (December 21, 2012). "The Evolution of BioShock Infinite". IGN. Archived from the original on March 18, 2020. Retrieved June 1, 2013.
- ^ Miller, Matt (April 9, 2013). "Free Will And Hope In BioShock Infinite". Game Informer. Archived from the original on January 1, 2014. Retrieved January 1, 2013.
Further reading
[edit]- Andersson, Rani-Henrik. The Lakota Ghost Dance of 1890. Lincoln, NE: University of Nebraska Press, 2009. ISBN 978-0803210738.
- Brown, Dee. Bury My Heart at Wounded Knee: An Indian History of the American West, Owl Books (1970). ISBN 0805066691.
- Craft, Francis M. At Standing Rock and Wounded Knee: The Journals and Papers of Father Francis M. Craft, 1888–1890, edited and annotated by Thomas W. Foley, Norman, Oklahoma: The Arthur H. Clark Company (2009). ISBN 978-0870623721.
- Champlin, Tim. A Trail To Wounded Knee : A Western Story. Five Star (2001).
- Coleman, William S.E. Voices of Wounded Knee, University of Nebraska Press (2000). ISBN 0803215061.
- Cozzens, Peter. The Earth is Weeping: The Epic Story on the Indian wars for the American West, Atlantic Books (2016) ISBN 978-1786491510.
- Foley, Thomas W. Father Francis M. Craft, Missionary to the Sioux, Lincoln, NE: University of Nebraska Press (2002). ISBN 0803220154.
- Gage, Justin. We Do Not Want the Gates Closed between Us: Native Networks and the Spread of the Ghost Dance. Norman: University of Oklahoma Press, 2020. ISBN 978-0806167251.
- Greene, Jerome A. (2014). American Carnage: Wounded Knee, 1890. Norman, OK: University of Oklahoma Press. ISBN 978-0-8061-4448-1.
- Hämäläinen, Pekka. Lakota America: A New History of Indigenous Power, New Haven, CT: Yale University Press (2019). ISBN 978-0300215953.
- Smith, Rex Alan. Moon of Popping Trees. Lincoln, NE: University of Nebraska Press (1981). ISBN 0803291205.
- Treuer, David. The Heartbeat of Wounded Knee : Native America from 1890 to the Present. New York: Riverhead Books (2019). ISBN 978-1594633157.
- Utley, Robert M. Last Days of the Sioux Nation. 2nd Edition New Haven, CT: Yale University Press (2004). ISBN 978-0300103168.
- Utley, Robert M. The Indian Frontier 1846–1890. Albuquerque, NM: University of New Mexico Press (2003). ISBN 0826329985.
- Utley, Robert M. Frontier Regulars The United States Army and the Indian 1866–1891. New York: Macmillan Publishing (1973). ISBN 0803295510.
- Yenne, Bill. Indian Wars: The Campaign for the American West, Westholme (2005). ISBN 1594160163.
External links
[edit](Pine Ridge Campaign).
- The Wounded Knee Museum in Wall, South Dakota
- "Walter Mason Camp Collection," includes photographs from the Battle of Wounded Knee Creek, Brigham Young University
- "A Dark Day" – Education Resource, Dakota Pathways
- "The Ghost Dance; How the Indians Work Themselves up to Fighting Pitch", eyewitness account by reporter, New York Times, November 22, 1890
- Army at Wounded Knee
- Remember the Massacre at Wounded Knee. Jacobin. December 29, 2016.
- 1890 in South Dakota
- 1890 murders in the United States
- 19th-century colonization of the Americas
- Anti-Indigenous racism in South Dakota
- Battles involving Native Americans
- Battles involving the Sioux
- Conflicts in 1890
- Conflicts in 1891
- December 1890 events
- History of South Dakota
- Lakota
- Last stands
- Massacres of Native Americans
- Massacres in 1890
- Mass graves in the United States
- Native American genocide
- Native American history of South Dakota
- Pine Ridge Campaign
- Sioux Wars
- United States military killing of American civilians